What is Static System?
A static system is a system that does not change over time. In other words, the output of a static system is not a function of time, but rather depends only on the current input to the system.
Static systems can be described using a mathematical model known as a static function, which maps an input signal to an output signal. These functions are typically represented using tables or graphs, which show the output of the system for different values of the input.
Static systems are often used to model simple physical systems, such as resistors in an electrical circuit or mechanical systems that are in equilibrium. They are relatively easy to analyze and design, as they do not exhibit time-dependent behavior.
Overall, static systems are an important concept in the field of signals and systems because they provide a simple way to model and understand the behavior of a wide variety of physical systems.
What is Dynamic System?
A dynamic system is a system that changes over time in response to external inputs or internal processes. In other words, the output of a dynamic system is a function of both the current input to the system and the past history of the system.
Dynamic systems can be described using a mathematical model known as a dynamic system model, which specifies how the system behaves over time in response to input signals. These models can take many different forms, including differential equations, difference equations, and state-space models.
Dynamic systems are often used to model complex physical systems, such as control systems, electronic circuits, and mechanical systems. They can exhibit a wide range of behaviors, including stability, oscillation, and instability.
Overall, dynamic systems are an important concept in the field of signals and systems because they provide a way to model and understand the behavior of systems that change over time in response to external inputs or internal processes.
Difference between Static and Dynamic System:
Text Version:
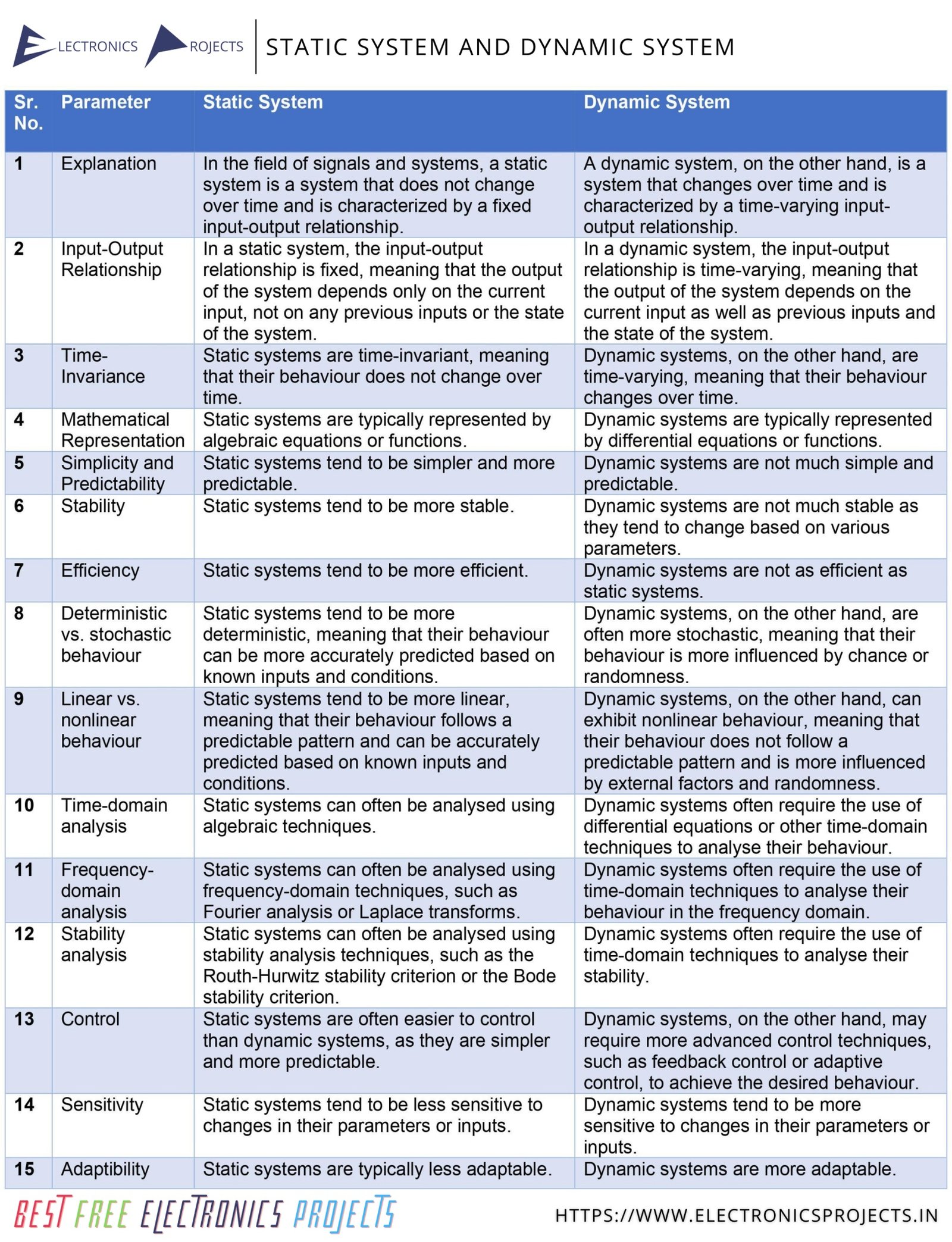
| SR. NO. | PARAMETER | STATIC SYSTEM | DYNAMIC SYSTEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Explanation | In the field of signals and systems, a static system is a system that does not change over time and is characterized by a fixed input-output relationship. | A dynamic system, on the other hand, is a system that changes over time and is characterized by a time-varying input-output relationship. |
| 2 | Input-Output Relationship | In a static system, the input-output relationship is fixed, meaning that the output of the system depends only on the current input, not on any previous inputs or the state of the system. | In a dynamic system, the input-output relationship is time-varying, meaning that the output of the system depends on the current input as well as previous inputs and the state of the system. |
| 3 | Time Invariance | Static systems are time-invariant, meaning that their behaviour does not change over time. | Dynamic systems, on the other hand, are time-varying, meaning that their behaviour changes over time. |
| 4 | Mathematical Representation | Static systems are typically represented by algebraic equations or functions. | Dynamic systems are typically represented by differential equations or functions. |
| 5 | Simplicity and Predictability | Static systems tend to be simpler and more predictable. | Dynamic systems are not much simple and predictable. |
| 6 | Stability | Static systems tend to be more stable. | Dynamic systems are not much stable as they tend to change based on various parameters. |
| 7 | Efficiency | Static systems tend to be more efficient. | Dynamic systems are not as efficient as static systems. |
| 8 | Deterministic vs Stochastic Behaviour | Static systems tend to be more deterministic, meaning that their behaviour can be more accurately predicted based on known inputs and conditions. | Dynamic systems, on the other hand, are often more stochastic, meaning that their behaviour is more influenced by chance or randomness. |
| 9 | Linear vs nonlinear behaviour | Static systems tend to be more linear, meaning that their behaviour follows a predictable pattern and can be accurately predicted based on known inputs and conditions. | Dynamic systems, on the other hand, can exhibit nonlinear behaviour, meaning that their behaviour does not follow a predictable pattern and is more influenced by external factors and randomness. |
| 10 | Time-Domain Analysis | Static systems can often be analyzed using algebraic techniques. | Dynamic systems often require the use of differential equations or other time-domain techniques to analyze their behaviour. |
| 11 | Frequency-Domain Analysis | Static systems can often be analysed using frequency-domain techniques, such as Fourier analysis or Laplace transforms. | Dynamic systems often require the use of time-domain techniques to analyse their behaviour in the frequency domain. |
| 12 | Stability Analysis | Static systems can often be analysed using stability analysis techniques, such as the Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion or the Bode stability criterion. | Dynamic systems often require the use of time-domain techniques to analyse their stability. |
| 13 | Control | Static systems are often easier to control than dynamic systems, as they are simpler and more predictable. | Dynamic systems, on the other hand, may require more advanced control techniques, such as feedback control or adaptive control, to achieve the desired behaviour. |
| 14 | Sensitivity | Static systems tend to be less sensitive to changes in their parameters or inputs. | Dynamic systems tend to be more sensitive to changes in their parameters or inputs. |
| 15 | Adaptability | Static systems are typically less adaptable. | Dynamic systems are more adaptable. |
Image Version:
Download above image in HD | Size: 1 MB | JPG Image
