What is Stable System?
A stable system is a system that behaves in a predictable and well-controlled manner when subjected to external inputs or disturbances. In other words, a stable system will exhibit a small, bounded change in its output in response to a small, bounded change in its input. This means that the system will not exhibit large, uncontrolled oscillations or diverge from its expected behavior.
There are several different ways to define stability in a system, depending on the context in which the system is being analyzed. Some common measures of stability include:
- Lyapunov stability: A system is Lyapunov stable if it returns to its equilibrium state after being perturbed by an external input.
- BIBO stability: A system is BIBO (bounded-input, bounded-output) stable if it produces a bounded output signal for any bounded input signal.
- Asymptotic stability: A system is asymptotically stable if it approaches its equilibrium state as the time goes to infinity.
Stability is an important concept in the field of signals and systems because it allows us to predict how a system will behave under different conditions and to design systems that exhibit the desired level of stability.
What is Unstable System?
An unstable system is a system that exhibits a large, uncontrolled change in its output in response to a small, bounded change in its input. This means that the system is sensitive to external perturbations and may exhibit large oscillations or diverge from its expected behavior.
There are several different ways to define instability in a system, depending on the context in which the system is being analyzed. Some common measures of instability include:
- Lyapunov instability: A system is Lyapunov unstable if it does not return to its equilibrium state after being perturbed by an external input.
- BIBO instability: A system is BIBO (bounded-input, bounded-output) unstable if it produces an unbounded output signal for a bounded input signal.
- Asymptotic instability: A system is asymptotically unstable if it does not approach its equilibrium state as the time goes to infinity.
Unstable systems can be difficult to analyze and control because they exhibit unpredictable behavior and may be sensitive to small changes in their input or operating conditions. As a result, stability is an important consideration in the design of systems in a wide range of fields.
Difference between Stable and Unstable System:
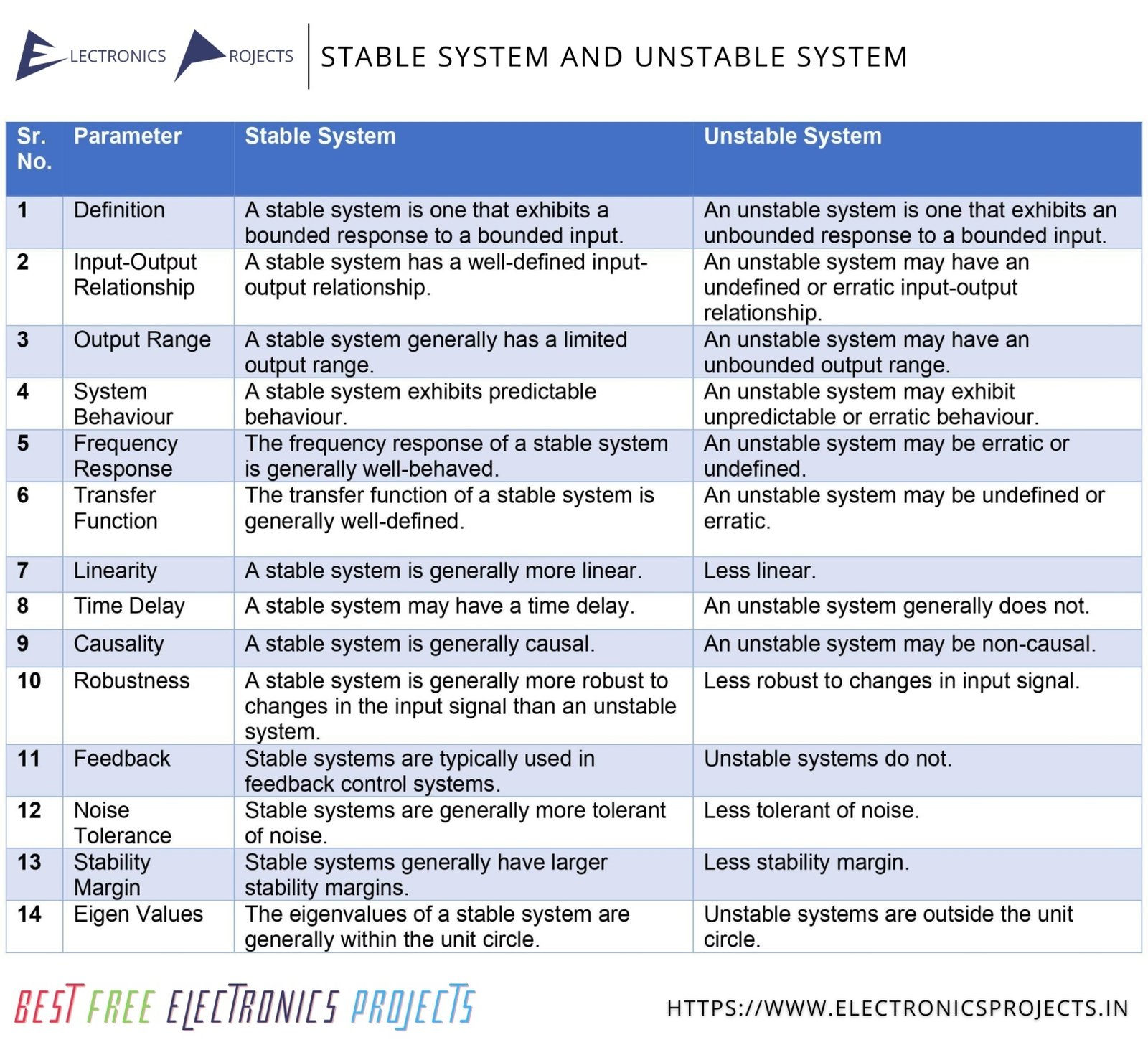
Text Version:
| SR. NO. | PARAMETER | STABLE SYSTEM | UNSTABLE SYSTEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Definition | A stable system is one that exhibits a bounded response to a bounded input. | An unstable system is one that exhibits an unbounded response to a bounded input. |
| 2 | Input-Output Relationship | A stable system has a well-defined input-output relationship. | An unstable system may have an undefined or erratic input-output relationship. |
| 3 | Output Range | A stable system generally has a limited output range. | An unstable system may have an unbounded output range. |
| 4 | System Behaviour | A stable system exhibits predictable behaviour. | An unstable system may exhibit unpredictable or erratic behaviour. |
| 5 | Frequency Response | The frequency response of a stable system is generally well-behaved. | An unstable system may be erratic or undefined. |
| 6 | Transfer Function | The transfer function of a stable system is generally well-defined. | An unstable system may be undefined or erratic. |
| 7 | Linearity | A stable system is generally more linear. | Less linear. |
| 8 | Time Delay | A stable system may have a time delay. | An unstable system generally does not. |
| 9 | Causality | A stable system is generally causal. | An unstable system may be non-causal. |
| 10 | Robustness | A stable system is generally more robust to changes in the input signal than an unstable system. | Less robust to changes in input signal. |
| 11 | Feedback | Stable systems are typically used in feedback control systems. | Unstable systems do not. |
| 12 | Noise Tolerance | Stable systems are generally more tolerant of noise. | Less tolerant of noise. |
| 13 | Stability Margin | Stable systems generally have larger stability margins. | Less stability margin. |
| 14 | Eigen Values | The eigenvalues of a stable system are generally within the unit circle. | Unstable systems are outside the unit circle. |
Image Version:
Download above image in HD | Size: 700 KB | JPG Image
